Working the ISS FM Repeater
A practical guide by N7FGP — Radios • Antennas • Doppler & Tuning • Tracking Software • Making a QSO

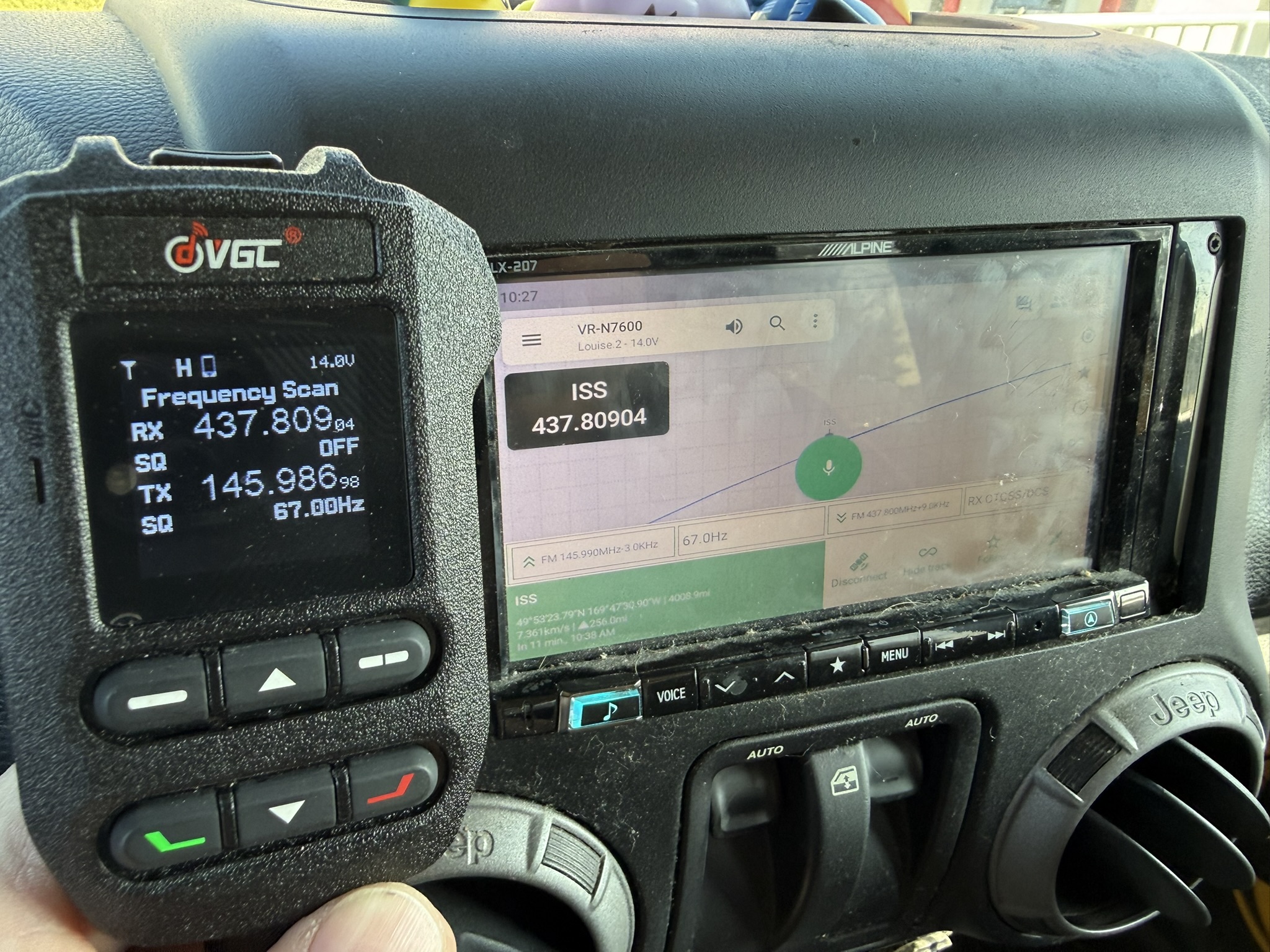
Radios
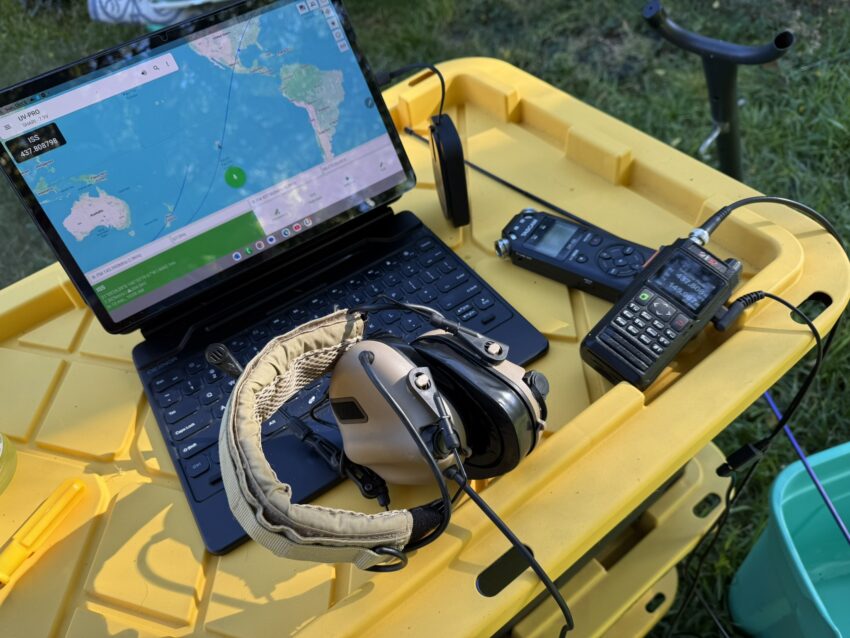
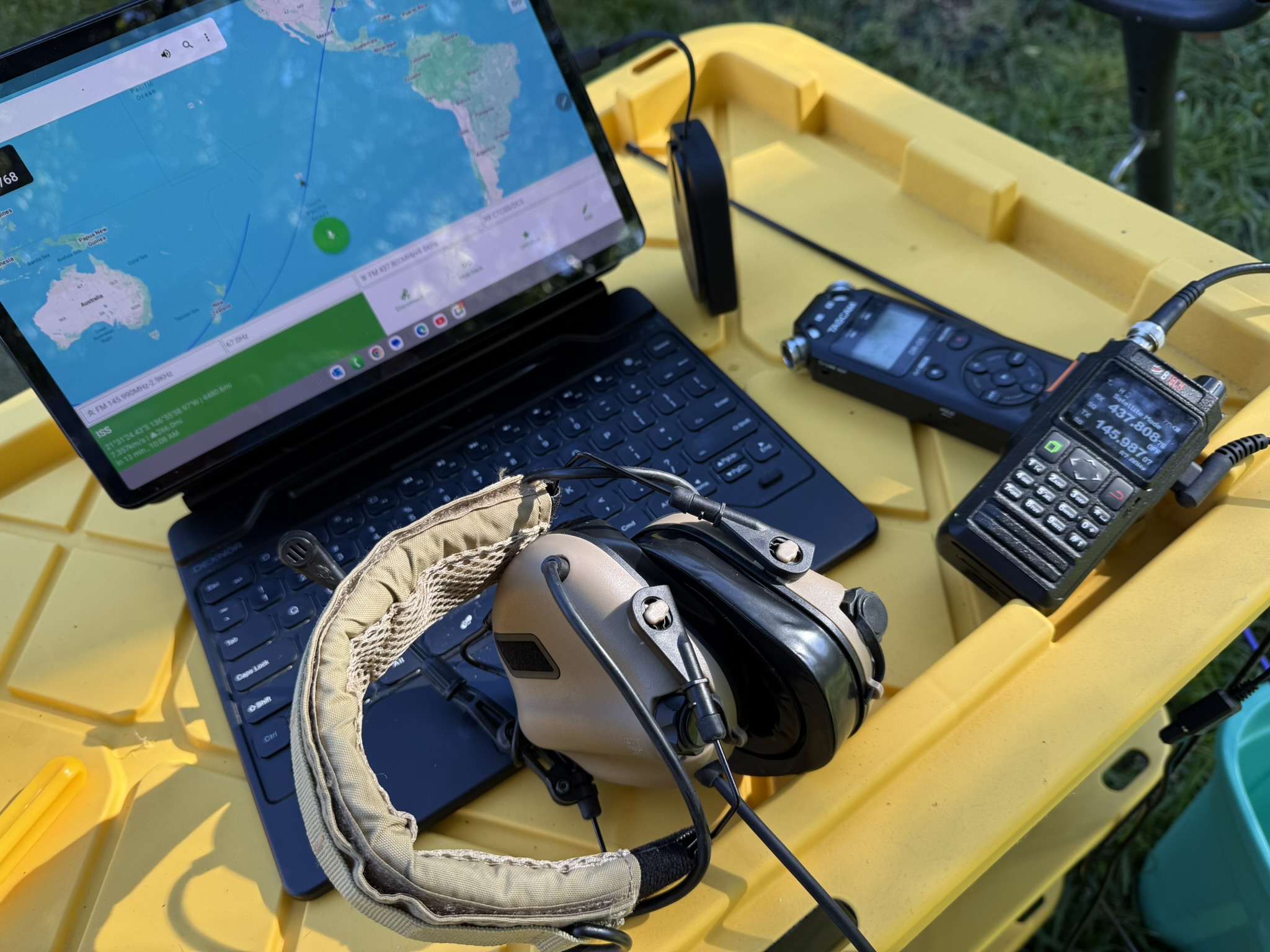
Quick picks: Entry: Vero/VGC VR‑N76 HT or VR‑N7600 mobile using the phone app’s satellite mode for auto‑Doppler. Full‑duplex: two‑radio setup, certain dual‑receiver mobiles, or the Icom IC‑9700 shack rig with Satellite mode (paired memories, AFC, SD recording).
Auto‑Doppler capable (handheld/mobile)
- Vero/VGC VR‑N76 (HT) — app‑driven satellite mode with Doppler auto‑stepping.
- Vero/VGC VR‑N7600 (mobile) — same app‑based auto‑Doppler in a 50‑W mobile form factor.
- AnyTone AT‑D878UVII Plus — satellite function with real‑time tracking & Doppler handling (update to recent firmware/CPS).
- AnyTone AT‑D168UV — real‑time satellite tracking with automatic Doppler adjustment (verify firmware/region).
Base multimode with sat conveniences
- Icom IC‑9700 — dedicated Satellite mode, paired uplink/downlink memories, and Automatic Frequency Control to follow Doppler on FM; records to SD.
Antennas
Small handheld beams (Arrow‑style Yagi, Elk‑style log‑periodic, or homebrew Cheap Yagi) are the easiest portable win. For hands‑off home monitoring, an eggbeater style omni with reflector kit gives near‑horizon coverage and an overhead lobe with fewer polarization fades.
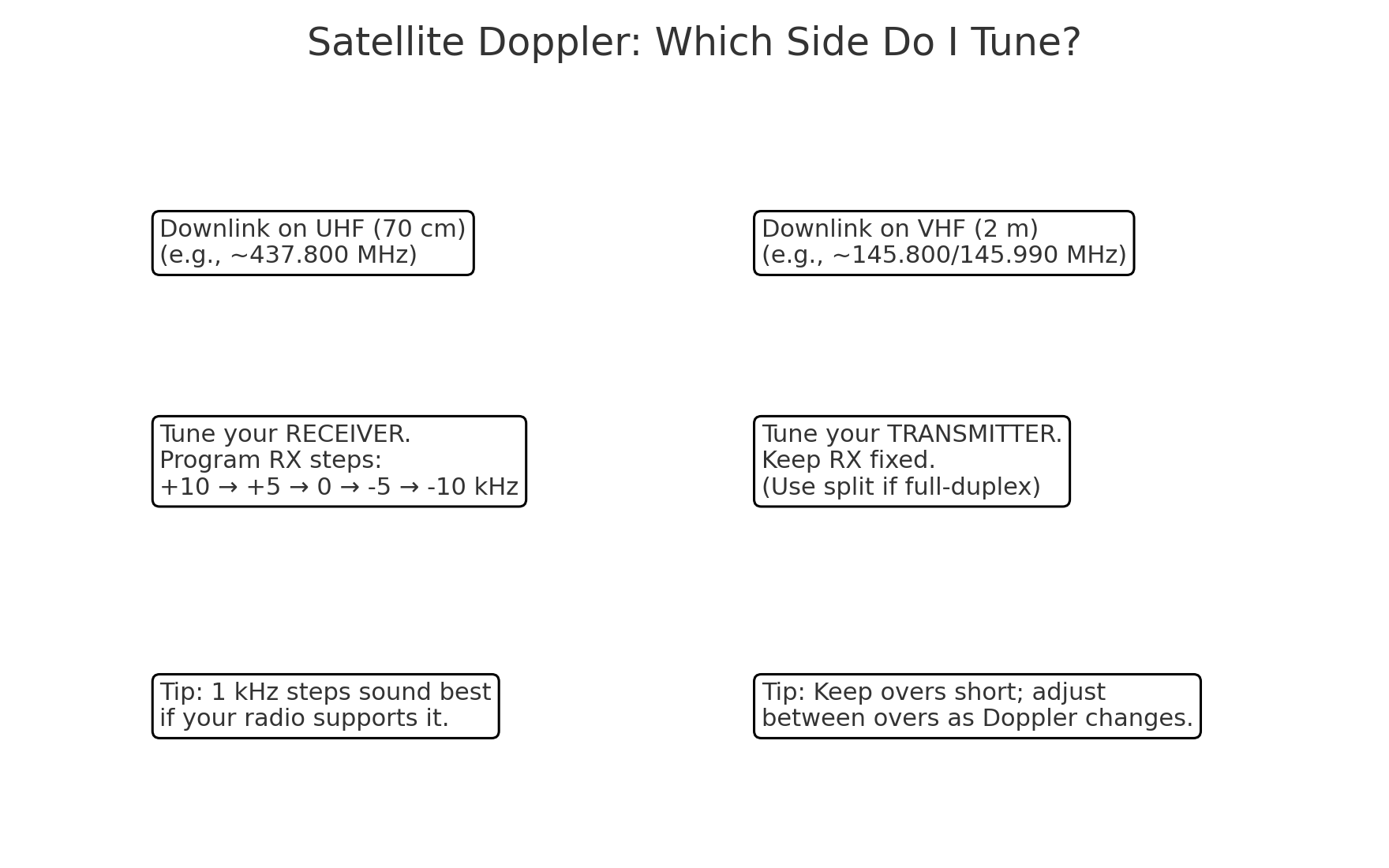
Doppler & How to Tune
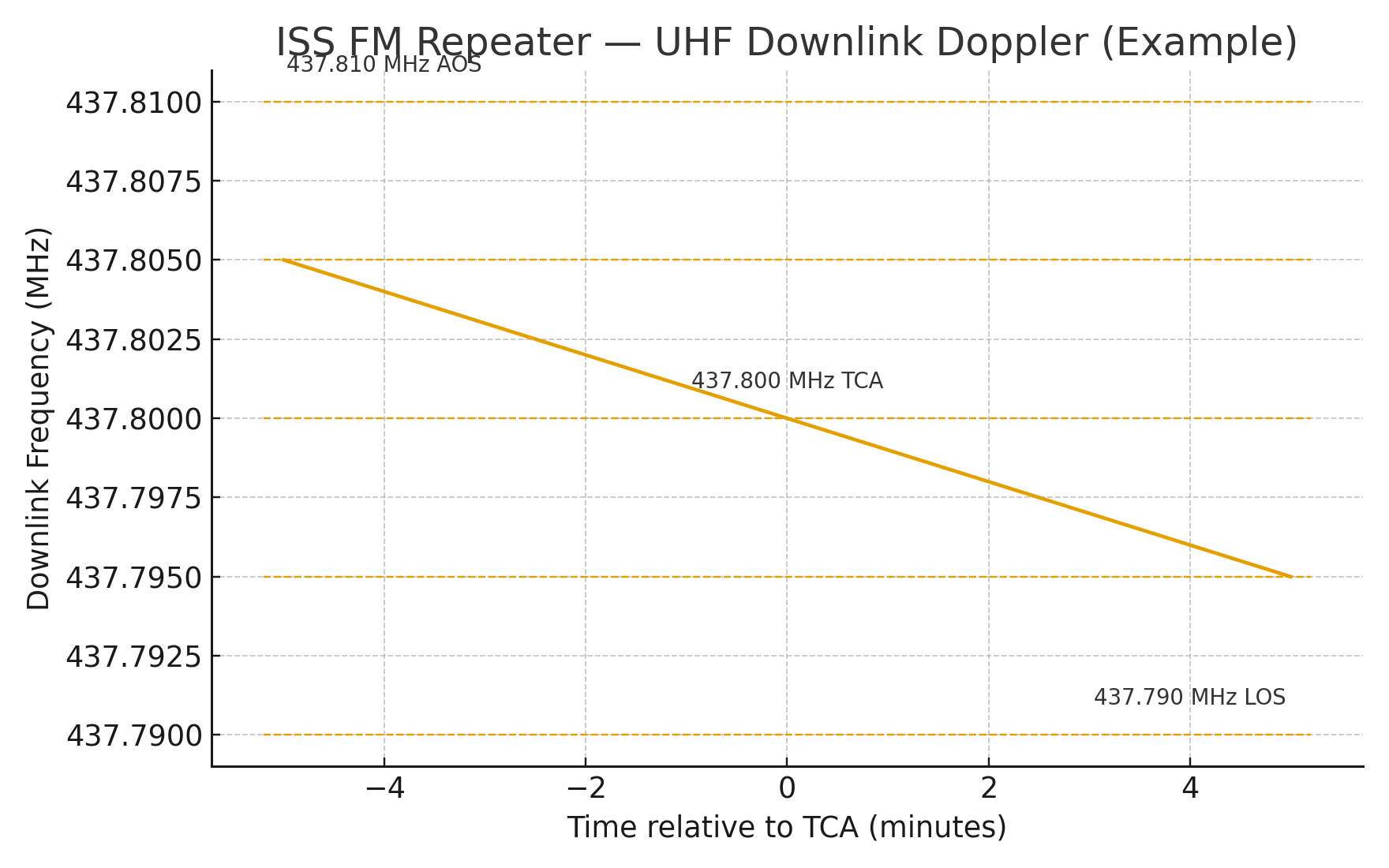
On 70 cm near 437.800 MHz, Doppler is ≈ ±10 kHz; on 2 m near 145.990 MHz, ≈ ±3 kHz. Stay centered or FM capture will let a stronger, better‑tuned station dominate.
- Five‑step RX plan (UHF downlink): 437.810 → 437.805 → 437.800 → 437.795 → 437.790 (AOS→LOS).
- Rule of thumb: UHF downlink → tune receiver; VHF downlink → tune transmitter.
- Full‑duplex: walk the downlink by ear while you talk; nudge +/‑1 kHz when your echo thins; twist polarization.
- Half‑duplex: keep overs 2–3 s; step one click between overs and listen for the hiss to drop.
Tracking Software
Use a tracker to pick good passes, keep your TLEs fresh, and, if desired, drive radio/rotor control.
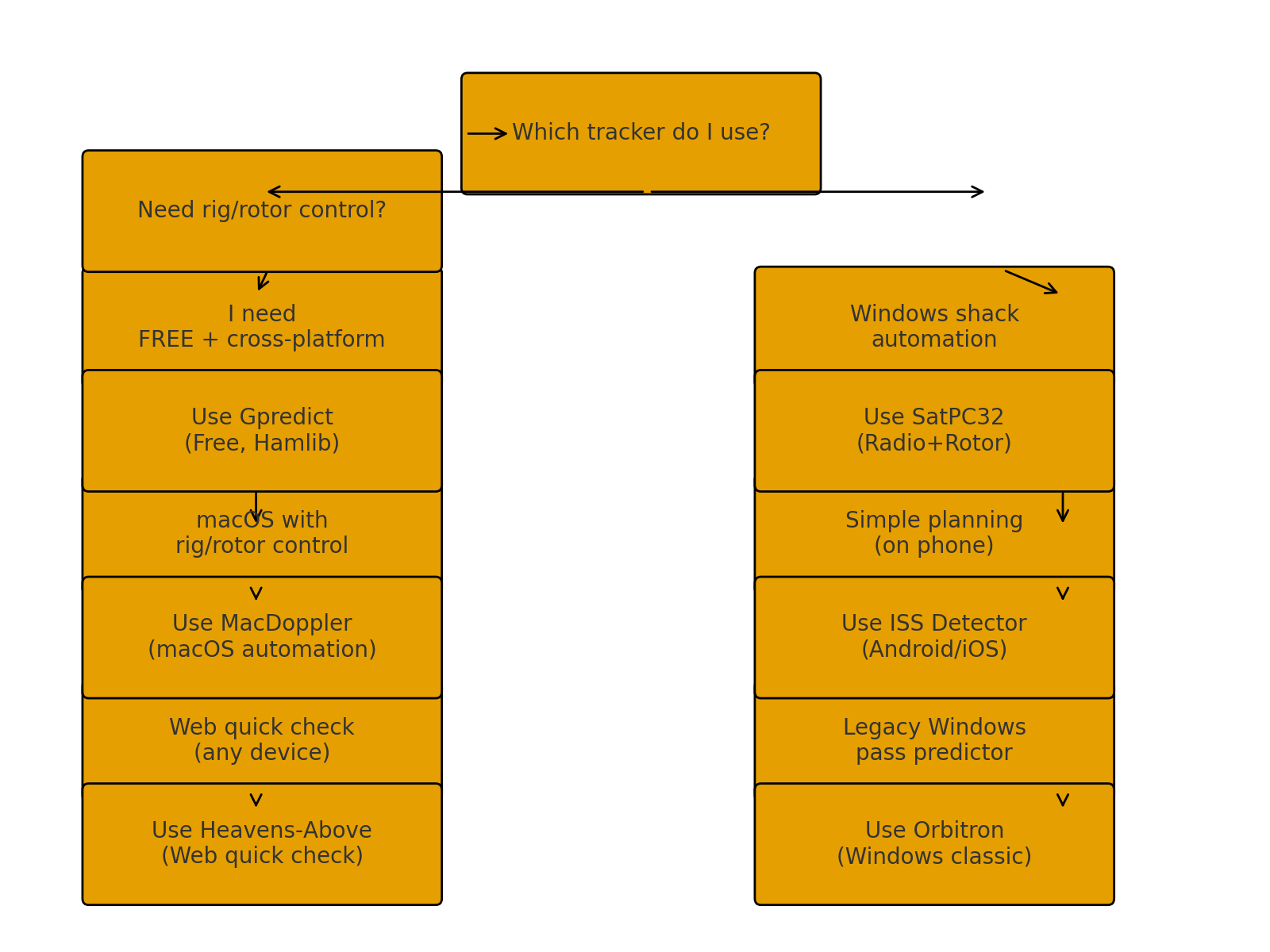
| Program | Platform | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Gpredict | Win • macOS • Linux | Free & open‑source; real‑time maps & pass tables; integrates with Hamlib for rig/rotor control. |
| SatPC32 | Windows | Long‑time AMSAT favorite; robust Doppler + rotor control (IC‑9700 et al.). |
| MacDoppler | macOS | Full station automation; polished UI; rotor control built‑in. |
| Orbitron | Windows | Free classic tracker; simple pass prediction on a shack PC. |
| Heavens‑Above | Web • Android • iOS | Fast, location‑based pass predictions and sky charts. |
| ISS Detector (Android) ISS Detector (iOS) |
Android • iOS | Great alerts; ham‑sat extension adds transmitter data and real‑time Doppler frequencies. |
| CelesTrak | — | Fresh TLEs (Two‑Line Elements). Keep these updated in any tracker you use. |
Making a QSO
Verify ops day‑of: typical repeater pair is uplink 145.990 MHz (CTCSS 67.0) and downlink 437.800 MHz, but always check ARISS status before the pass.
On‑air rhythm: Short 2–3 s overs keep the pass fair and let you retune—say “CALL CALL, MYCALL GRID,” stop, listen, adjust, go again. FM capture rewards the station that is centered and clean more than the one that is simply loud.
